
In the kinematic measuring method, gravity is the only force that acts on the sample. The mass (or weight) of a fluid is determined by gravity. Therefore, we say that steel has a greater density than ice cube. They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube. Think about an ice cube and a cube of steel. Dynamic (cP) / Density = Kinematic (cSt)įor a given sample, with a density greater than one, dynamic viscosity will always be the higher number.ĭensity is the ratio of the mass (or weight) of the sample divided by the volume of the sample.Kinematic (cSt) x Density = Dynamic (cP) A converting table between viscosity units like Centiposes, milliPascal, CentiStokes and SSU.Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. Because the dynamic viscosity of real fluids is invariably a fractional quantity, the more usual unit is the centipoise (cP, 10-3 N s m-2) and is represented by the Greek letter eta (). The non-SI, but acceptable unit, the Poise, is 0.1 N s m-2. The unit of measure of kinematic viscosity is Centistokes (cSt).Ī basic difference between the dynamic and kinematic viscosity measurements is density. unit of dynamic viscosity is a Newton second per square metre or Pascal second (N s m-2 or Pa s). The result from the formula is often expressed as centipoise and commonly abbreviated as cP (one-hundredth of a poise). The time is converted directly to kinematic viscosity using a calibration constant provided for the specific tube. There are several ways to find the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, but the most common method is determining the time it takes a fluid to flow through a capillary tube. cP to gram-force second/square centimeter cP to millipoise cP to dyne-second/square centimeter cP to reyn cP to newton-second. Water has a viscosity of 0.0089 poise at 25 ☌, or 1 centipoise at 20 ☌. A centipoise is one millipascal second (mPa·s) in SI units.
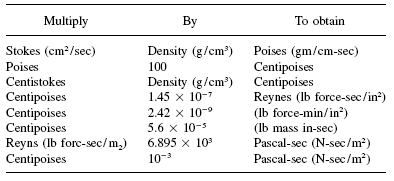
Put another way, kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s inherent resistance to flow when no external force, except gravity, is acting on it. A unit of dynamic viscosity in the CGS system of units. The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. Water at 20 ☌ has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt. Other units are: 1 St ( Stoke) = 1 cm 2/s = 10 −4 m 2/s. The SI unit of the kinematic viscosity is m 2/s. The kinematic viscosity is the ratio between the dynamic viscosity and the density of a fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
